
Calories and weight gain are closely connected, yet many people do not fully understand how excess calories lead to fat storage, belly fat, and long-term health problems.
Weight gain is one of the most common health concerns today. Many people struggle with stubborn belly fat, unexplained weight increase, or difficulty losing weight despite “eating small.” At the center of this issue is one simple but often misunderstood concept: calories.
Calories are not the enemy. In fact, your body needs calories to survive. However, consistently consuming more calories than your body needs leads to weight gain over time. Understanding how calories work—and how they affect fat storage, hormones, blood sugar, and metabolism—is key to maintaining a healthy weight.
This pillar guide explains everything you need to know about calories and weight gain in a simple, practical way.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Are Calories?
Calories are units of energy. They measure how much energy your body gets from food and drinks. According to the World Health Organization, excess calorie intake contributes significantly to overweight and obesity worldwide (WHO, 2023).
Your body uses calories to:
Breathe
Pump blood
Digest food
Move muscles
Support hormone production
Maintain body temperature
Even when you are sleeping, your body is burning calories to keep you alive.

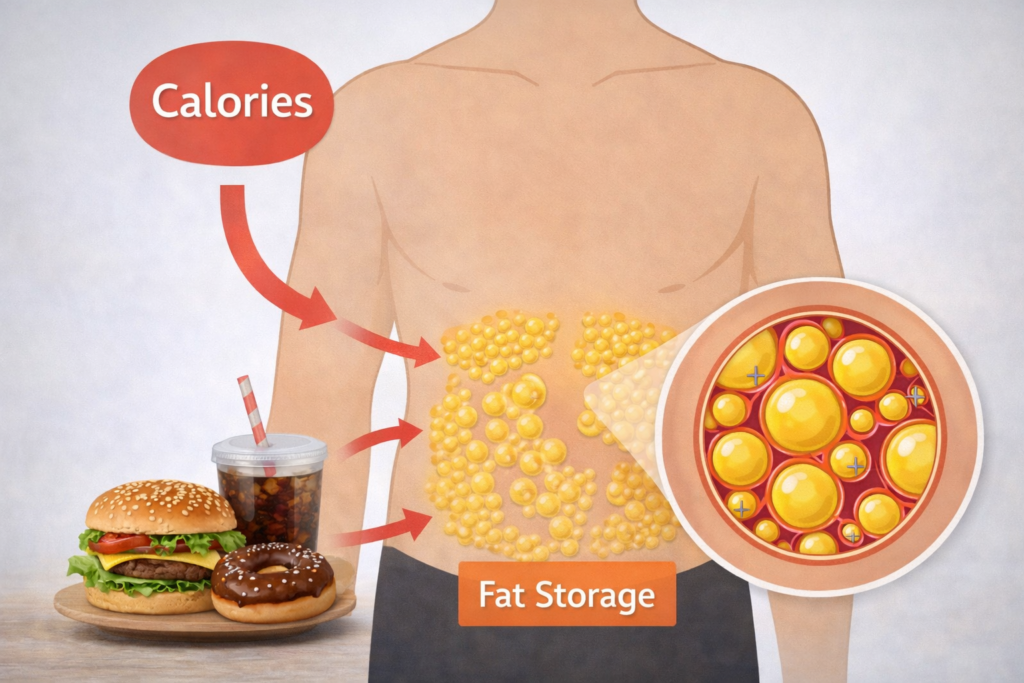
How Calories Lead to Weight Gain and Fat Storage
Weight gain happens when your body receives more calories than it burns. This is known as a calorie surplus. The NHS explains that consuming more calories than the body burns leads to gradual weight gain over time (NHS, 2024).
When excess calories are not used for energy:
They are stored as fat
Fat storage often occurs around the belly, hips, thighs, and arms
Over time, this leads to gradual weight gain
This process is not immediate—it happens slowly and steadily.
Calorie Intake vs Calorie Burn
Your body burns calories in three main ways:
1. Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
This is the energy your body uses at rest for vital functions like breathing and circulation.
2. Physical Activity
Walking, exercising, house chores, and daily movement burn calories.
3. Digestion (Thermic Effect of Food)
Your body burns calories just by digesting and absorbing food.
If calorie intake consistently exceeds all three combined, weight gain occurs.
Common High-Calorie Foods That Cause Weight Gain
Some foods are easy to overeat because they are high in calories but low in satiety.
Examples include:
Sugary drinks and fruit juices
Pastries, cakes, biscuits
Fried foods
Fast food
Large portions of white rice, bread, and pasta
Processed snacks
These foods do not keep you full for long, leading to overeating.

Calories vs Food Quality
Not all calories affect the body in the same way.
Example:
300 calories from soda → quick blood sugar spike, hunger returns fast
300 calories from eggs and vegetables → fullness, stable blood sugar
Highly processed foods:
Increase hunger
Disrupt hormones
Promote fat storage
Whole foods:
Improve satiety
Support metabolism
Help regulate appetite
Calories and Hormones
Calories influence hormones that control hunger and fat storage.
When calorie intake is poor or excessive:
Insulin resistance increases
Leptin (satiety hormone) becomes ineffective
Cortisol (stress hormone) promotes fat storage
This is why stress eating and poor sleep often lead to weight gain—even without large meals.
Calories and Belly Fat
Excess calorie intake is strongly linked to visceral fat, also known as belly fat.
Belly fat is dangerous because it:
Increases insulin resistance
Raises blood pressure
Increases inflammation
Raises the risk of heart disease
Sugary foods, refined carbohydrates, and late-night overeating are major contributors.

Calories and Blood Sugar Control
For people with diabetes or prediabetes:
Excess calories worsen insulin resistance
High-calorie refined carbs spike blood sugar
Weight gain further increases diabetes risk
Balanced meals with controlled calories help:
Stabilise blood sugar
Improve insulin sensitivity
Support healthy weight management
👉 Diabetes Causes, Symptoms & Management (VeeVee Health)

Calories and High Blood Pressure
Excess calorie intake often leads to:
Weight gain
Increased sodium intake
Increased strain on the heart
Managing calories through whole foods supports:
Healthy blood pressure
Reduced heart disease risk
Daily Calorie Needs (General Guide)
Calorie needs vary by age, gender, activity level, and metabolism.
General Estimates:
Sedentary women: 1,800–2,000 calories
Active women: 2,000–2,200 calories
Sedentary men: 2,200–2,400 calories
Active men: 2,400–2,800 calories
These are guidelines, not strict rules.
Why Weight Gain Is Common Today
The World Health Organization explains that excess calorie intake contributes significantly to overweight and obesity worldwide.
Modern lifestyles encourage excessive calorie intake through:
Large portion sizes
Frequent snacking
Sugary drinks
Sitting for long hours
Stress and poor sleep
Many people consume excess calories without realising it.
Calorie Myths You Should Ignore
Myth 1: Eating less always leads to weight loss
✔ Hormones and metabolism matter
Myth 2: Fat should be avoided
✔ Healthy fats are essential
Myth 3: All calories are equal
✔ Food quality matters
Sustainable Weight Management with Calories
Managing calories and weight gain requires
Awareness, not restriction
Balance, not deprivation
Consistency, not perfection
Healthy calorie management supports:
Stable weight
Better energy
Improved blood sugar
Heart health
Healthy Ways to Reduce Calorie-Related Weight Gain
You don’t need extreme dieting. Small consistent changes matter.
Practical Tips:
Eat slowly and mindfully
Start meals with protein
Increase vegetables and fibre
Reduce sugary drinks
Watch portion sizes
Move your body daily

Final Thoughts on Calories and Weight Gain
Calories are essential for life, but excess calories over time lead to weight gain. Understanding how calories work empowers you to make healthier food choices, manage weight naturally, and protect your long-term health.
At VeeVee Health, we focus on sustainable, culturally relevant, and realistic lifestyle changes.
👉 Want personalised help managing calories for weight loss, diabetes, or blood pressure?
👉 Explore more resources on www.veeveehealth.com or book a consultation today.
References
References:
NHS (2024). Managing your weight.
World Health Organization (2023). Obesity and overweight.
Balancing our meals and exercising is a good one.
thanks for your response
ebemada111@gmail.com
Calories are just numbers, it’s the quality of your food that truly matters, understanding this concept can lead to a healthier lifestyle
thanks for your response
Calories are just numbers, but your hard work and dedication are what truly matter
Sure!
Calories work empower you to make healthier food choices, manage weight naturally, and protect your long term health
Thank you!
Thank you
Calories plays a Significant role in overall health and wellness. The roles of Calories in weight gain is Multifaceted.
Excess calories intake is strongly linked to visceral fat also known as belly fat
Thank you!
Thank you
Walk and exercise does a lot in cutting down calories.
Calories plays a Significant role in overall health and wellness. The roles of Calories in weight gain is Multifaceted.
Pingback: 7 Common High-Calorie Foods That Cause Weight Gain You Should Avoid | VeeVee Health
Pingback: 8 Unhealthy Foods Nigerian Children Eat Today