Diabetes is one of the fastest-growing chronic health conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people across all age groups. It occurs when the body is unable to properly regulate blood glucose (sugar) levels, either due to insufficient insulin production, ineffective use of insulin, or both. When left unmanaged, diabetic condition can lead to serious complications affecting the heart, kidneys, eyes, nerves, and overall quality of life.
According to the World Health Organization, the condition is a major cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, stroke, and lower-limb amputation globally . In the UK and many African countries, Type 2 diabetes is increasing rapidly due to lifestyle changes, dietary patterns, physical inactivity, and rising obesity rates.
This comprehensive guide explains what this metabolic condition is, its causes, types, signs and symptoms, risk factors, and most importantly, how it can be effectively managed and prevented.
Table of Contents
ToggleWHAT IS DIABETES?
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterised by persistently high levels of glucose in the blood. Glucose is the body’s main source of energy and comes from the foods we eat, especially carbohydrates. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps move glucose from the bloodstream into the body’s cells where it is used for energy.
When insulin is absent, insufficient, or ineffective, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to hyperglycaemia (high blood sugar). Over time, uncontrolled hyperglycaemia damages blood vessels and organs.
TYPES OF DIABETES
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body produces little or no insulin.
Key features:
Often diagnosed in children and young adults
Requires lifelong insulin therapy
Not caused by lifestyle factors
Although the exact cause is unknown, genetic predisposition and environmental triggers are believed to play a role .

Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form, accounting for over 90% of the disease cases worldwide. It develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to meet the body’s needs. The World Health Organization reports that diabetic condition is a major global public health concern.
Key features:
Strongly linked to overweight, obesity, and physical inactivity
More common in adults but increasingly seen in younger people
Can often be managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin
In African and Caribbean populations, Type 2 diabetes often develops at a younger age and at lower body weights compared to other populations .
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes interfere with insulin action. It usually resolves after childbirth, but it significantly increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life for both mother and child.
Other Specific Types
These include:
Monogenic diabetes (caused by single gene mutations)
Diabetes due to pancreatic disease
Drug-induced diabetes (e.g., long-term steroid use)
.
CAUSES OF DIABETES
According to the NHS, high blood sugar is diagnosed using blood tests such as HbA1c and fasting glucose. Diabetes develops due to a combination of genetic, biological, and lifestyle factors.
Biological Causes
Insulin deficiency
Insulin resistance
Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic cells
Lifestyle-Related Causes
Diets high in refined carbohydrates and sugary drinks
Physical inactivity
Excess visceral (belly) fat
Chronic stress and poor sleep patterns
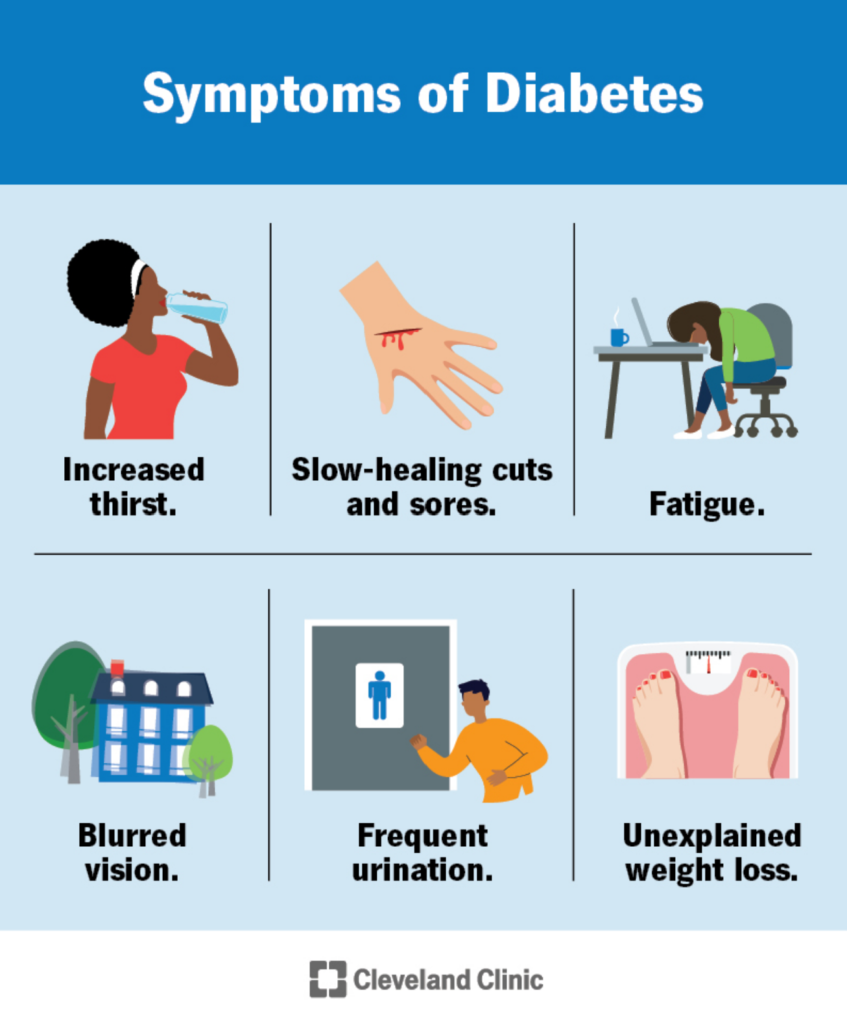
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF DIABETES
Many people live with undiagnosed high blood sugar because symptoms may develop gradually, especially in Type 2 diabetes.
Common Symptoms
Frequent urination
Excessive thirst
Persistent hunger
Unexplained weight loss
Fatigue and weakness
Blurred vision
Slow-healing wounds
Recurrent infections
Advanced Symptoms
Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
Erectile dysfunction
Darkened skin around the neck or armpits (acanthosis nigricans)
Early diagnosis is crucial to prevent long-term complications .
RISK FACTORS FOR DIABETES
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
- Family history of diabetes
- Age over 35–40 years
Ethnicity (African, Caribbean, South Asian descent)
History of gestational condition
Modifiable Risk Factors
Overweight and obesity
Poor diet quality
Physical inactivity
Smoking
Excess alcohol intake
Chronic stress

DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETES
Diabetes is diagnosed through blood tests such as:
Fasting plasma glucose
HbA1c test
Oral glucose tolerance test
The NHS recommends regular screening for people with risk factors .
MANAGEMENT AND CONTROL OF DIABETES
Individuals with high blood sugar focuses on maintaining blood glucose levels within a healthy range to prevent complications.
Healthy Nutrition
A balanced diet is central to high blood sugar control:
Emphasise whole grains, vegetables, legumes, and lean protein
Limit refined sugars and ultra-processed foods
Combine carbohydrates with protein and fibre to reduce glucose spikes
👉
Best Nigerian Foods for Managing Diabetes
Physical Activity
Regular movement improves insulin sensitivity:
At least 150 minutes of moderate activity weekly
Walking, strength training, and flexibility exercises
Weight Management
Even modest weight loss (5–10%) significantly improves blood sugar control in Type 2 diabetes .
Intermittent fasting can also help to reduce weight thereby helping to manage type 2 diabetes
Medications and Insulin
Some individuals require:
Oral glucose-lowering medications
Injectable therapies
Insulin therapy (Type 1 and advanced Type 2)
Medication should always be individualised and supervised by healthcare professionals.
Monitoring Blood Sugar
Self-monitoring helps individuals understand how food, stress, and activity affect glucose levels.
COMPLICATIONS OF UNCONTROLLED DIABETES
Poorly managed diabetes can lead to:
Heart disease and stroke
Kidney failure
Vision loss
Nerve damage
Foot ulcers and amputations
Early control significantly reduces these risks .
PREVENTION OF TYPE 2 DIABETES
Diabetes UK emphasises lifestyle changes as key to prevention.
Up to 80% of Type 2 diabetes cases are preventable through lifestyle changes:
Healthy eating
Regular physical activity
Maintaining a healthy waist circumference
Managing stress and sleep
Diabetes is one of the fastest-growing chronic health conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people across all age groups. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and management options is essential for preventing complications and improving quality of life.
CONCLUSION
Blood sugar disorder is a serious but manageable condition. With early diagnosis, proper education, healthy lifestyle choices, and appropriate medical care, people living with diabetes can lead full, active, and healthy lives. Public awareness, culturally appropriate dietary guidance, and community education—especially within African and Caribbean populations—are essential in reversing the growing diabetes burden.
At VeeVee Health, our goal is to empower you with practical, evidence-based health information that supports long-term wellbeing.
REFERENCES
World Health Organization. Diabetes Fact Sheet
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Types of Diabetes
International Diabetes Federation. Diabetes and Ethnicity
NHS UK. Symptoms and Diagnosis of Diabetes
Diabetes UK. Weight Management and Diabetes
WHO. Diabetes Complications
🧠 Quick Diabetes Knowledge Quiz
Answer the questions below to see how well you understand diabetes.
Please can you explain more on type 2 diabetes?
Thank you
Prevention they say is better than cure. Thank you for this prevention and management tips
The best summary I’ve read on diabetes. Thank you 👍, kudos
I believe you in every of your teachings
God bless you always. Compliments of the season. 🎅 🎄 ❤️ Doc.
Which food is recommended for someone with diabetes?
Pingback: Understanding High Blood Pressure: Causes, Symptoms, and What It Means for Your Health
Pingback: Calories and Weight Gain: What You Should Know for Healthy Living
I nice one keep it up vevee health
Keep up sharing
Keep up sharing vevee health
Diabetes is a serious manageable condition. A balanced diet is central diabetes control to combine carbohydrates with protein and fiber to reduce glucose spikes.
Diabetes is a serious but manageable Condition that requires a lot work and dedication to control and manage properly, but with right mindset and support is possible.
Thanks for your response
Stay positive and keep moving forward.
Pingback: 7 Common High-Calorie Foods That Cause Weight Gain You Should Avoid | VeeVee Health
Eat Moderate and more of veggies. Be active in physical exercise and stay hydrated!💪
Pingback: 8 Early Signs of Diabetes You Should Not Ignore (Silent Warning Signs)
Pingback: 7 Everyday Habits That Raise Blood Sugar (Even If You’re Not Diabetic)
Thanks for this wonderful teaching.
Pingback: Best Nigerian Foods for Managing High Blood Pressure (10 Healthy options)
Pingback: Top 10 Nigerian Fruits for Diabetes (Local & Blood Sugar Friendly)